Tower cranes are the backbone of modern construction, but their efficiency hinges on proactive maintenance and tower crane safety training. According to the International Crane Foundation, 23% of crane failures stem from neglected wear-prone components, leading to costly downtime and safety risks. This guide explores critical wear parts, inspection workflows, and safety precautions for tower crane operations to maximize equipment lifespan and worksite safety.

Common Wear-Prone Parts List & Failure Causes
Understanding the vulnerabilities of a tower crane begins with identifying its most susceptible components:
1. Wire Ropes & Hooks
Failure Signs: Broken wires, kinks, or flattened sections.
Root Causes: Overloading, abrasive contact with sheaves, or exposure to corrosive environments.

2. Brakes & Reducers
Failure Signs: Delayed braking, grinding noises, or oil leaks.
Root Causes: Overheating from frequent stops, contaminated lubricants, or worn brake linings.

3. Pulley Assemblies & Bearings
Failure Signs: Uneven groove wear, seized rotation, or abnormal vibrations.
Root Causes: Dust accumulation, inadequate greasing, or misalignment.

4. Electrical Components
Failure Signs: Flickering controls, blown fuses, or burnt insulation smells.
Root Causes: Moisture ingress, vibration-induced wire fatigue, or voltage spikes.
5. Connecting Bolts & Pins
Failure Signs: Rust streaks, loose fasteners, or hairline cracks.
Root Causes: Vibration fatigue, improper torque application, or galvanic corrosion.
6. Safety Devices (Limit Switches, Load Moment Limiters)
Failure Signs: False alarms, delayed responses, or unresponsive controls.
Root Causes: Sensor misalignment, software glitches, or damaged wiring.
7. Structural Components (Standard Sections, Jibs)
Failure Signs: Visible cracks, weld defects, or localized bending.
Root Causes: Overloading, wind-induced stress, or material fatigue.
2. Comprehensive Inspection Workflow for Wear-Prone Parts
Daily Checks (Operators)
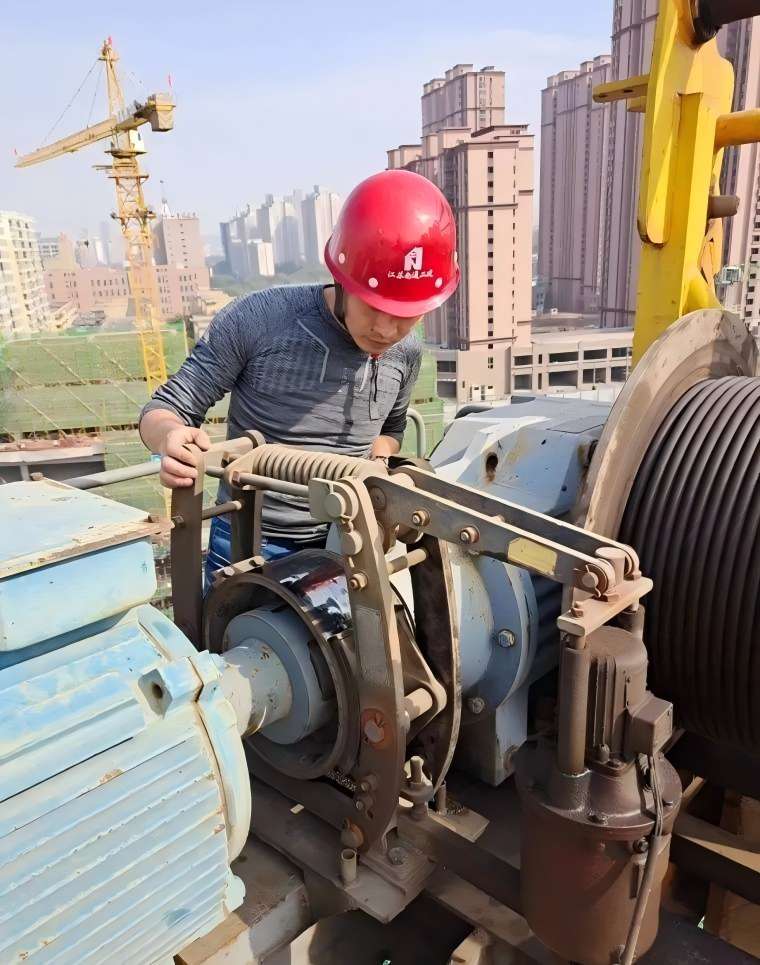

Key Tasks: Conduct thorough inspections by applying the ’10-diameter rule’ to wire ropes (replacing if six or more wires are broken within one lay length), verifying brake responsiveness through no-load lift tests, and confirming limit switch functionality at 95% of maximum reach.
Safety Integration: Daily checklists reinforce safety precautions for tower crane by mandating PPE like harnesses during climb inspections.
Periodic Inspections (Monthly/Quarterly by Professionals)
Critical Actions: To ensure optimal performance and safety, reducers should be disassembled for gear tooth wear checks against ISO 6336 tolerances, bearing clearance measured with dial indicators and replaced if exceeding 0.15mm, and megger tests conducted on electrical circuits, maintaining a minimum 1MΩ insulation resistance.
Training Tie-In: OSHA-compliant tower crane safety training certifies inspectors to interpret these technical measurements accurately.
Post-Extreme Condition Checks
Post-Storm Checks: Inspect foundation bolts for loosening caused by soil erosion. Use inclinometers to detect tower verticality deviations >1/500 of height.
Post-Overload Protocol: Perform magnetic particle testing (MPI) on load-bearing welds. Recalibrate load moment limiters using certified test weights.
Digital Inspection Technologies
Drone Inspections: Capture 4K imagery of jib sections inaccessible via traditional methods.
Predictive Analytics: Vibration sensors paired with AI algorithms predict bearing failures 200+ hours in advance.
Safety Synergy: These tools reduce technician exposure to fall hazards – a vital safety precaution for tower crane maintenance.
Maintenance Techniques to Extend the Lifespan of Tower Crane Wear Parts
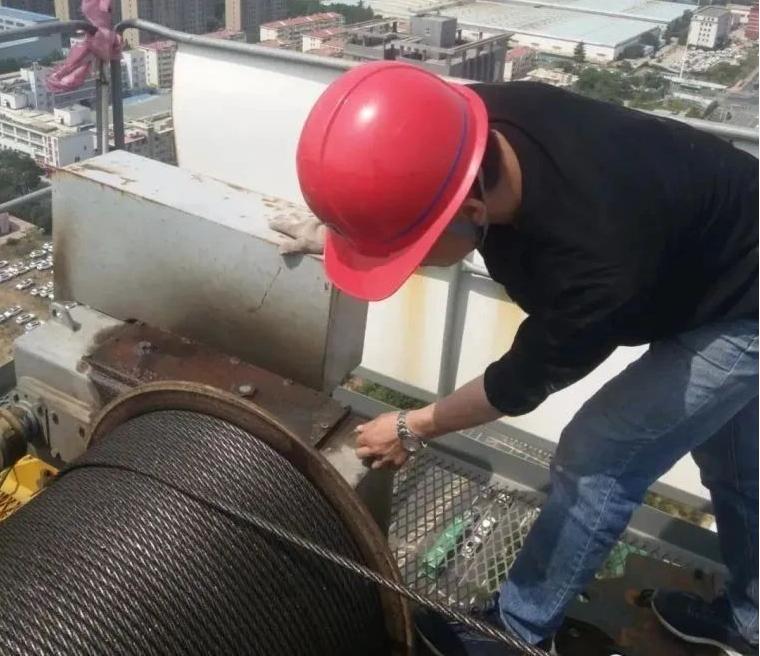

Proactive maintenance is the cornerstone of extending tower crane lifespan:
- Lubrication: Regular lubrication of moving parts reduces friction and wear. Use the correct lubricants as specified by the manufacturer.
- Cleaning: Keeping components clean prevents the accumulation of dirt and debris, which can accelerate wear.
- Tightening: Regularly check and tighten bolts and connections to prevent loosening.
- Replacement: Replace worn or damaged parts promptly with genuine manufacturer components.
- Proper Operation: Avoid overloading the crane and operate it within its design parameters.
- Tower crane safety training: Ensuring that all operators and maintenance personnel receive comprehensive tower crane safety training is essential. This training should cover proper operation, inspection procedures, and emergency protocols.
- Safety precautions for tower crane: Adhering to strict safety precautions for tower crane operations is crucial. This includes implementing lockout/tagout procedures, maintaining safe working distances, and conducting regular safety meetings.
Summary

Extending the lifespan of a tower crane requires a proactive approach to maintenance and inspection. By understanding the common wear-prone parts, implementing a comprehensive inspection workflow, and adhering to strict maintenance techniques, construction companies can ensure the safe and efficient operation of their equipment. When replacements are necessary, partnering with a reliable tower crane parts supplier is crucial to guarantee the use of high-quality, compatible components.
Furthermore, investing in thorough tower crane safety training and enforcing stringent safety precautions for tower crane operations are indispensable for preventing accidents and creating a secure work environment. Regular checks, professional inspections, and the use of modern digital inspection technologies are all vital parts of a good maintenance program. By prioritizing these measures, you can maximize the return on your investment and minimize the risk of costly downtime and accidents.
Related Products
Tower Crane Slewing Device
Smooth Operation
Export directly without 3RD company
Slewing Ring for Tower Crane
Best quality based on…
Centrifugal Fan for Slewing Mechanism
Simple design
Prevents overheating
Ensures smooth operation
Slewing Reducer for Tower Crane
Best quality based on…