As the core component of lifting equipment, the safety condition of crane wire ropes directly affects the safety of the entire operation process. According to statistics, approximately 20% of crane accidents are related to defects in steel wire ropes. Therefore, it is particularly important to have a thorough understanding of the damage standards of wire ropes and their preventive strategies. Mastering the standards for wire rope damage is not only an essential skill for special equipment operators but also an important line of defense for ensuring safe production. This article will provide a detailed introduction to the common damage types of crane wire ropes, inspection procedures, and practical maintenance tips, helping you accurately identify the safety status of the steel wire ropes.
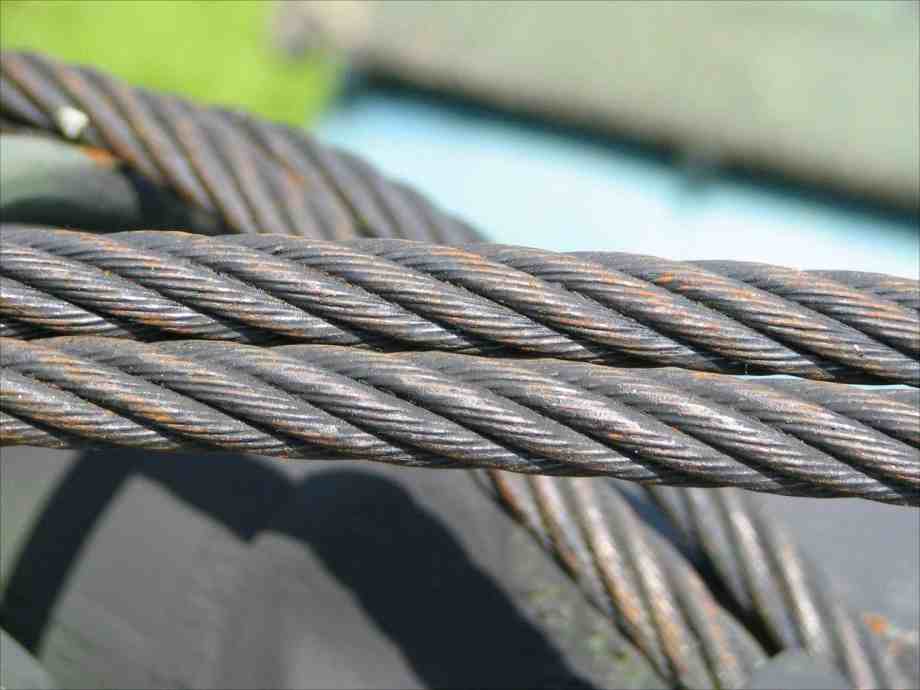

Wire Rope Construction and Classification
To understand damage, one must first understand the object itself. A crane wire rope is a sophisticated piece of engineering designed for strength and flexibility.
Basic Structure of Wire Ropes
A wire rope is composed of three main components:
| Component | Description |
| Wires | Individual steel strands that provide tensile strength. |
| Strands | Bundles of wires twisted together to form the rope’s main body. |
| Core | The central element supporting the strands. Divided into two types: fiber core (FC) and steel core (WC) |
Each component contributes to the overall strength, flexibility, and durability of the rope. Understanding the structure is the first step in identifying potential damage.
Common Types of Wire Ropes
Wire ropes vary depending on their construction, flexibility, and intended application:
- Rotation-resistant ropes – Designed to minimize twisting under load.
- Standard lifting ropes – Most common in general crane operations.
- Galvanized or coated ropes – Offer corrosion resistance in harsh environments.
- Specialized ropes – Such as compacted ropes or ropes for high-temperature applications.
Six Common Damage Types of Crane Wire Ropes
Crane wire ropes are subject to multiple forms of damage. Recognizing these crane wire rope damage types early can prevent accidents and costly downtime.
2.1 Abrasion
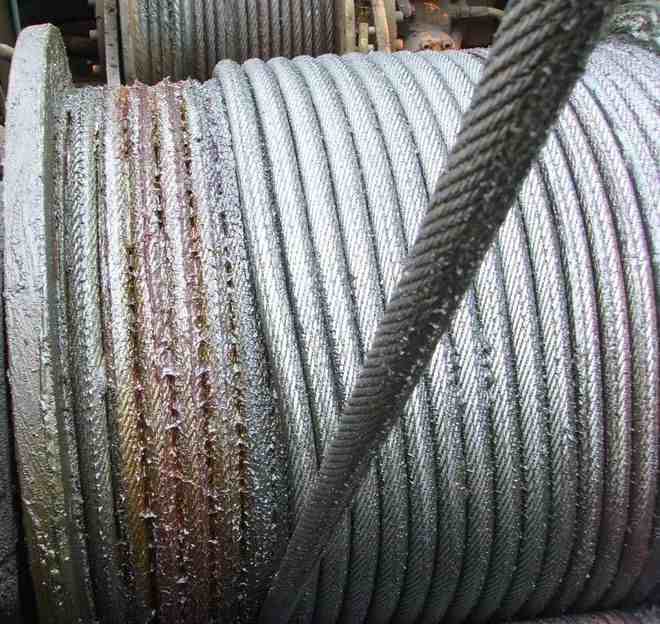

During the operation of steel wire ropes, wear is a common fault of wire ropes. Their surfaces are constantly subjected to multiple effects such as mechanical, physical and chemical ones, leading to wear. Wear mainly falls into two types: internal wear and external wear.
- Internal wear: Due to the concentrated pressure of the load inside the steel wire rope, the contact stress between the wires increases, resulting in internal wear, which is particularly significant during bending.
- External wear: When the steel wire rope is in operation, its outer periphery will rub against the surfaces of objects such as pulley grooves. This wear will gradually narrow the rope diameter and reduce its load-bearing capacity.
Wear and tear will reduce the strength of steel wire ropes. When it reaches 40%, they need to be scrapped.
2.2 Broken Wires
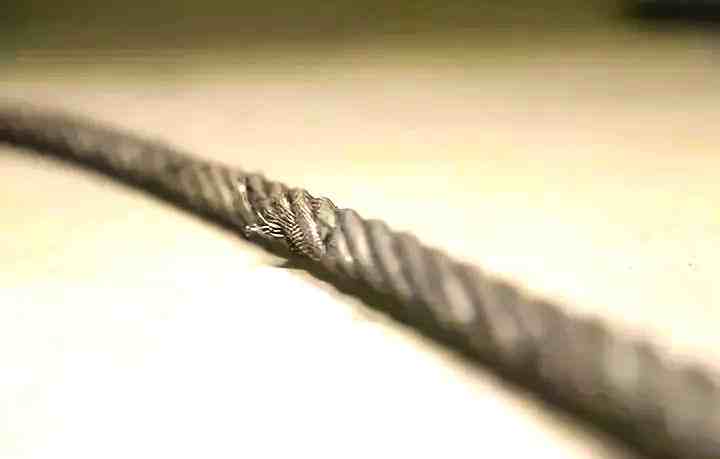

The broken wires of steel wire ropes are caused by long-term use and excessive stress, especially on the outer surface and inside multi-strand structures. Broken wires can affect the load-bearing capacity of steel wire ropes. If not dealt with promptly, it may lead to sudden breakage of the steel wire rope. The cause should be identified and it should be considered whether the broken wire part needs to be cut off and reinstalled.
- Parietal broken wires: If there are two broken wires within one lay length or the number of broken wires reaches 10% of the total number of wires (for example, more than 12 broken wires in a 6×19 structural steel wire rope), it should be scrapped immediately.
- Bone hook broken wires: Broken wires at the connection of rope strands directly weaken the strength of key parts and must be stopped immediately.
- Concentrated broken wires: If the same strand of broken wires reaches 5% within a length six times the rope diameter, it shall be scrapped at double the standard.
2.3 Crushing or Kinking
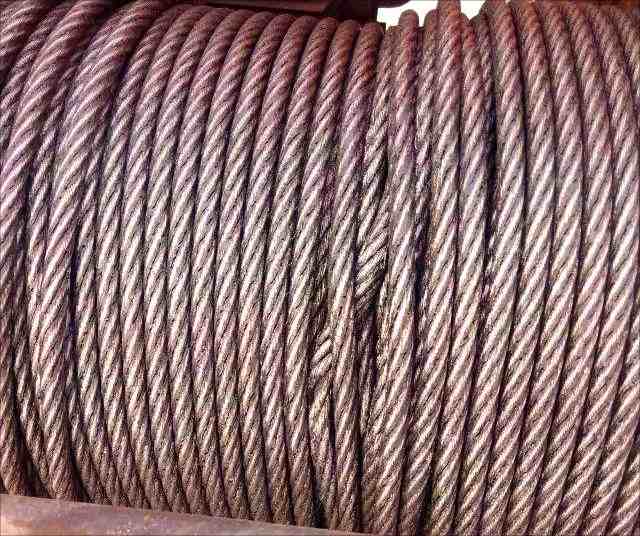

Excessive pressure, bypassing small pulleys or improper operation may cause the rope to be squeezed or knotted. When local lifting of the steel wires or exposure of a single strand core appears on the surface of the steel wire rope, it indicates that the internal structure has been severely damaged and it should be scrapped immediately. Such defects are mostly caused by overloading or improper installation.
2.4 Corrosion / Rusting
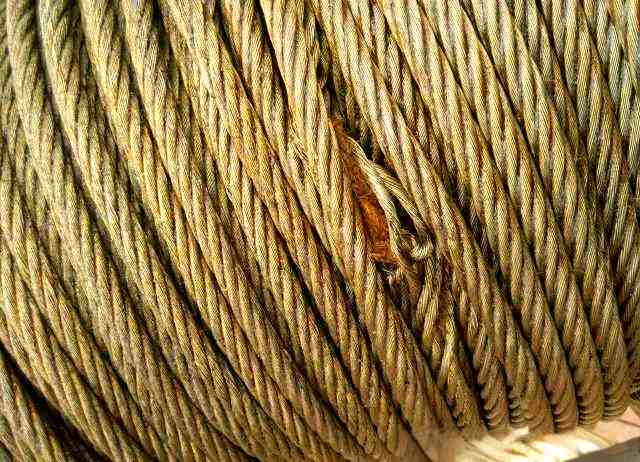

Corrosion is prone to occur in Marine or industrial-polluted atmospheres. It not only reduces the metal area of steel wire ropes, lowers their breaking strength, but also causes surface roughness, crack development and accelerates fatigue. External corrosion can be observed with the naked eye, while internal corrosion is more difficult to detect. However, it can be identified through changes in the diameter of the steel wire rope, reduction in the gap between the outer strands, and the accompanying broken wires and other phenomena.
Galvanized or coated steel wire ropes can resist corrosion, but regular inspection remains crucial. If any signs of internal corrosion are found, an internal inspection should be carried out. Once severe internal corrosion is confirmed, the vehicle should be scrapped immediately.
2.5 Strand Separation / Birdcaging
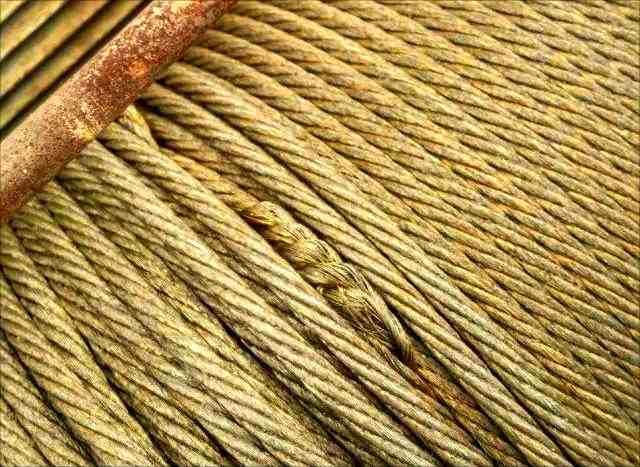

When the steel wire rope undergoes wavy deformation with the peak height exceeding 25% of the diameter, or when the outer steel wires spread out in a cage-like pattern, it indicates that the internal strands have lost their binding force. This is usually caused by overloading or improper handling. Once the birdcage phenomenon occurs, the rope should be replaced immediately.
2.6 Kinking and Snagging
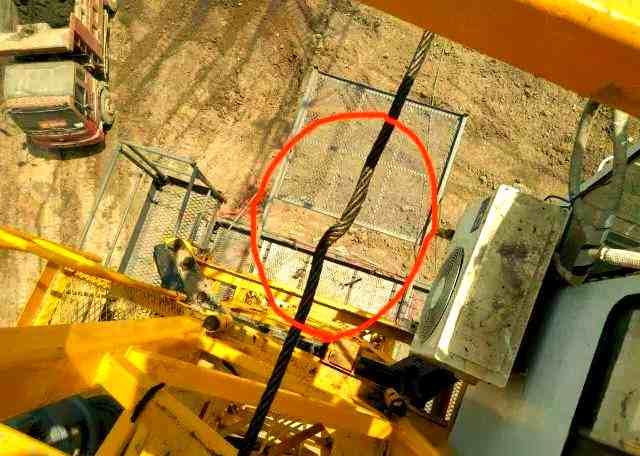

Kinking occurs when the rope is bent sharply or caught on obstacles. Snagging refers to entanglement during operation. Both create stress points that may accelerate fatigue and damage.
Inspection Process and Damage Assessment of Wire Ropes
Regular inspection is critical to prevent accidents caused by crane wire rope damage. A comprehensive inspection process includes:
Check the tool preparation
- Wire Rope flaw detector
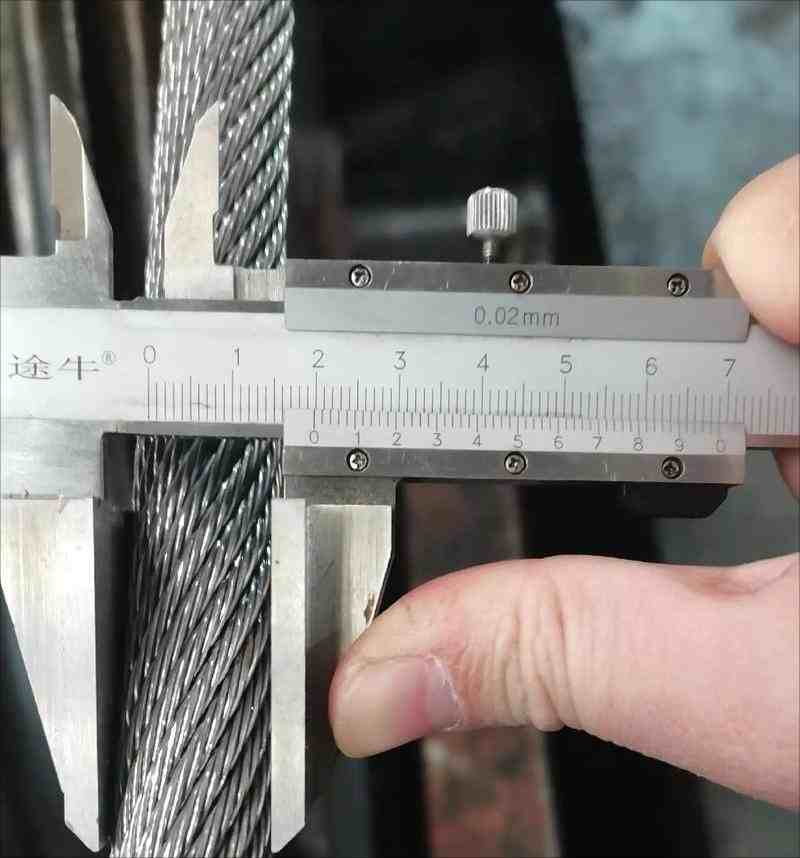
- Vernier caliper (accuracy 0.02mm)
- Marker pen
- Strong light flashlight
- Gloves and cleaning cloths
Standardize the inspection process

1. Clean the surface: Wipe the section to be inspected with a cloth
2. Visual inspection: Move slowly along the length of the rope and observe the surface condition
3. Manual inspection: Wear gloves and slowly run through the steel wire rope to sense any abnormality
4. Diameter measurement: Select three different positions for measurement and record
5. Broken wire counting: Focus on inspecting suspicious areas
6. Internal inspection: Bend appropriately to observe the condition of the internal steel wire
Practical Tips for Wire Rope Protection and Maintenance
Sound maintenance is the key to extending the life of a wire rope and ensuring safety.
- Regular Lubrication: Employ the appropriate lubricant at regular intervals. It protects the strands and core from corrosion within and reduces friction.
- Correct Winding: Wind and spool the wire rope correctly onto the drum. Incorrect winding results in crushing, kinking, and uneven wear.
- Avoid Shock Loads: Sudden, out-of-control application of force can be very destructive. Always lower and lift loads in a smooth motion.
- Regular Sheave and Drum Inspection: Ensure sheaves and drums are in good condition with no grooves, rusting, or worn bearings which could destroy the rope.
- Correct Storage: When a rope is not in use for a long period, store it in a clean dry location, away from corrosive chemicals.
Conclusion

Accurately judging the damage condition of crane steel wire ropes is a professional skill that requires the combination of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. Operators should cultivate a safety awareness of “doubting everything” and remain highly vigilant about the condition of the steel wire rope. Remember: When there are any doubts about the condition of the steel wire rope, the safest option is always to replace it rather than take the risk of continuing to use it.
For companies and operators seeking high-quality wire ropes and professional maintenance solutions, CPTC offers comprehensive crane wire ropes, inspection services and safety guidance to ensure reliable lifting operations. Investing in proper maintenance and timely replacement of steel wire ropes is not only a safety measure but also a cost-saving strategy in the long run.
Safety Notice: The standards provided in this article are for general reference only. When implementing them specifically, the recommendations of the equipment manufacturer and the latest relevant standards should be followed. Steel wire rope inspection should be carried out by trained and qualified professionals, and the inspection results should be recorded and archived.
Related Products
Tower Crane Pinion – 99/38/19 teeth
Steel Wire Rope | CPTC-CHINA
Casting Tower Crane Pulley
High strength;…
Tower Crane Hoisting Device
Smooth operation, precise control
Highly adaptable