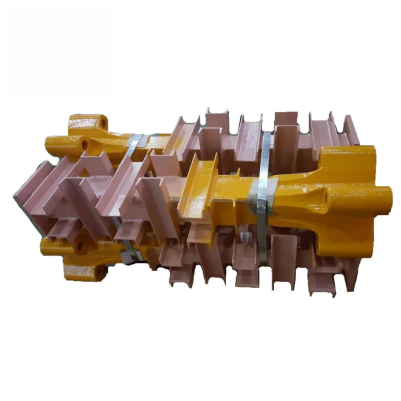
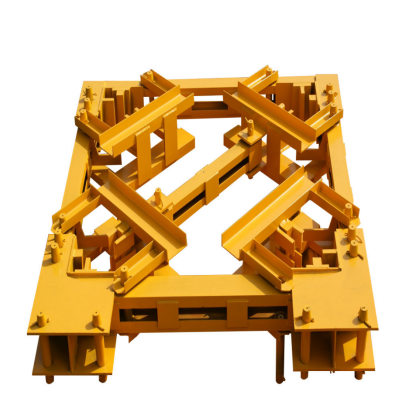
The mast section in a tower crane is the structural column of each tower crane that sustains the height, stability and strength required to lift heavy loads in the working site. It is important to know the dimensions of tower crane masts to ensure proper compatibility, safe operation and efficient assembly. The main mast height of a tower crane varies as per various types and brands of tower cranes, and there is no global standard. Then here in this article, we will inform you about some common mast section sizes of tower cranes to make it easy for you to choose the correct mast section for your project.

Decoding Common Tower Crane Mast Section Sizes and Models
Mast sections consist of lattice steel frames, usually square in cross-section, bolted or pinned together to achieve the required working height. They are standardized in dimensions, though there may be slight differences in specification between makers. Size is usually quoted by cross-section dimension (width × width) and by the length of one segment.
Categorization by Cross-Section
Tower crane mast sections are generally categorized based on the size of their cross-section, which is directly proportional to the maximum bending moment and axial load they carry.
Small/Light Duty (e.g., 1.2m×1.2m): For smaller tower cranes such as self-erecting ones or those with medium capacity and low free-standing height. An example is the Potain S24 series.
Standard/Medium Duty (e.g., 1.6m×1.6m): This is arguably the most prevalent size globally. It provides a compromise between acceptable lifting capacity and height performance and acceptable transport cost and erection logistics. Models usually associated with this size are the Potain L44 and L46 series.
Heavy Duty/High-Rise (e.g., 2.0m×2.0m and above): Needed for tall, heavy-duty cranes used in constructing super-tall buildings. Bigger sizes offer a lot more stiffness and strength, enabling larger free-standing heights and heavier lifting moments. Famous examples include the Potain L68 series.
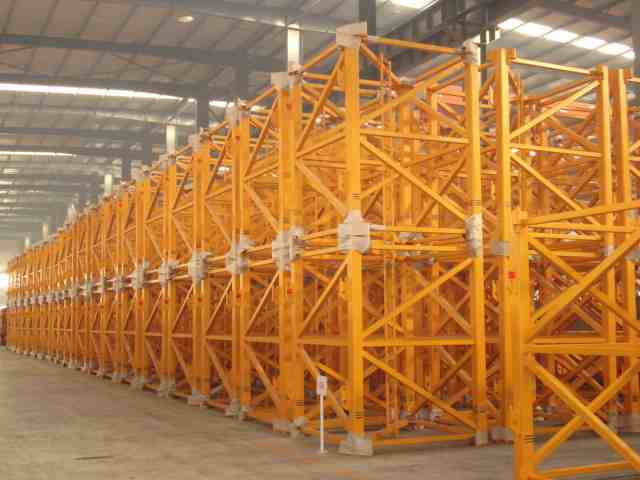

The Specification Table
To illustrate the technical differences, here is a breakdown of common, industry-standard mast section specifications. Note that the mast section’s size (cross-section) and the specifications of its main chord (the vertical steel member at the corner) are the key determinants of its load-bearing capacity.
| Crane Series/Brand | Typical Model | Dimensions (Cross-Section × Length) | Approx. Weight (kg) | Typical Main Chord Specification | Pin/Bolt Diameter (mm) | Typical Application |
| Potain (Light) | S24 | 1.2m×1.2m×3.0m | ≈850 | Varies | D40 / D45 | Small to Medium Cranes |
| Potain (Medium) | L46A1 | 1.6m×1.6m×3.0m | ≈1180 | ∠180×18 | D50 | Mid-Range Capacity Cranes |
| Potain (Heavy) | L68B1 | 2.0m×2.0m×3.0m | ≈1400 | ∠200×20 | D55 | Heavy-Lift, High-Rise Projects |
| Liebherr (Example) | 132HC | 1.8m×1.8m×2.5m | Varies | Varies | Varies | Large Cranes |
The dimensions are typically the outer edge measurements of the square cross-section.
Critical Factors for Selecting the Correct Mast Section Size
The selection of mast section is more than just picking a figure; it is a detailed analysis of the structural and functional needs of the project.
1. Required Lifting Capacity and Radius (Load Moment)
The largest consideration is the load moment (force applied at a distance). A crane with a longer jib or one required to lift heavy loads at a greater radius must be built on a larger, stronger mast section.
A broader cross-section provides a larger lever arm, which significantly enhances the resistance of the crane to bending stresses caused by the load. Widening from a 1.6m section to a 2.0m section, for example, provides a significant improvement in rigidity and load capacity.
2. Maximum Free-Standing Height
Maximum free-standing height (the height to which the crane is permitted without being mounted to a building) is limited by mast buckling strength.
Larger Mast Size = Greater Free-Standing Height: The larger the cross-section, the much greater moment of inertia, i.e., the tower can be built higher without tie-ins. This is necessary for the first high-rise construction phases before the building structure becomes anchoring-ready.
3. Brand Compatibility and Interchangeability

Mast sections ARE NOT interchangeable across the board, although the cross-sectional sizes might appear to be similar. Interchangeability depends on:
Connection Design: Different brands (e.g., Potain, Liebherr, Zoomlion) utilize different connection plates, pin diameters (e.g., D50mm vs. D55mm), bolt hole configurations, and bolts.
Structural Certification: Mixing components of differing manufacturers may nullify structural warranties and safety certifications. When replacing or extending pieces, they must be precisely the same as OEM specifications and strength or be certified as an entirely compatible replacement part by a reputable supplier.
4. Manufacturing Quality and Material Grade
Mast section stability depends on construction quality. The key quality criteria are:
Steel Grade: Generic high-quality tower crane masts utilize Q345B (or its international equivalent, S355), which has high yield strength necessary for high-rise structures.
Weld Quality: Automated and certified welding must be present to ensure that joints—where the principal chord, web members, and connection plates meet—are free of defects causing fatigue failure.
CPTC: Your Partner in Crane Safety and Efficiency
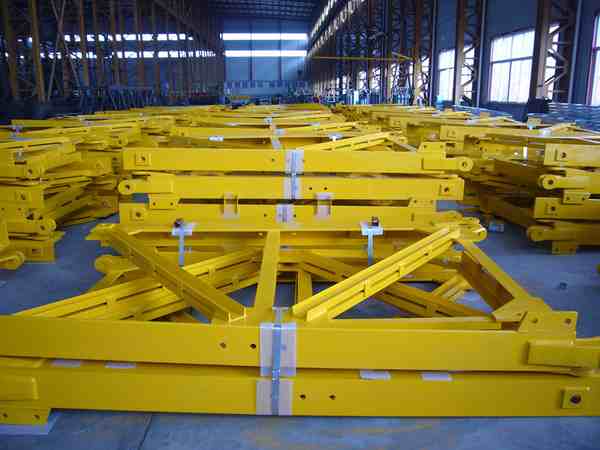

As a construction expert, an understanding supplier able to value the sophistication of mast section fabrication is central to long-term operation efficiency and safety. At CPTC, we are committed to providing mast sections that not only comply but exceed the performance requirements of top OEM models through rigorous engineering design and quality control.
- Precision Fabrication: We have expertise in fabricating totally compatible replacement mast sections for leading companies like Potain so that the main dimensions and attachment points of our parts are an exact replica of the original component. Our manufacturing process involves the latest fixtures and fixtures to maintain rigid tolerances, mainly in pin hole alignment, which is critical to safety and ease of assembly.
- Fine material control: We purchase only quality Q345B structural steel and conduct factory certification testing on each shipment of goods. Through such commitment, the yield point and toughness of the steel can meet the requirement for high-stress crane use, especially in poor weather conditions.
- Optimized design and testing: Our design team is committed to the optimization of truss structure geometry and main chord member thickness, and also the web member thickness (also referred to as supports). Each component has been thoroughly tested through non-destructive testing (NDT) for load-carrying welds specifically, to validate strength and longer service life.
Contact our engineers today to ensure that your tower crane’s main structure is able to bear load in the future.
Related Article:
What Is a Tower Crane Mast Section? Everything You Should Know
How Many Sections Does a Tower Crane Mast Have?
Related Products
All Kinds of Tower Crane Fixing Angle
Good stability
Lightweight
Fishing Plate for Tower Crane Fixing Angle
Tower Crane Mast Section
Steel pipe construction
Comprehensive spare parts
Safety, stability, reliability
Tower Crane Wall Tie
Vertical support
Safety enhancement