Gearboxes are essential but subject to wear and tear like any complex gear. Gearbox failure has severe consequences, including costly downtime, safety hazards, and even property damage. To circumvent these dangers, regular inspections are essential to identify and correct likely problems ahead of time, so we can have confidence in the continued stability and safety of our hoists. In this piece, we will look at the major steps involved in conducting a thorough hoist gearbox inspection.

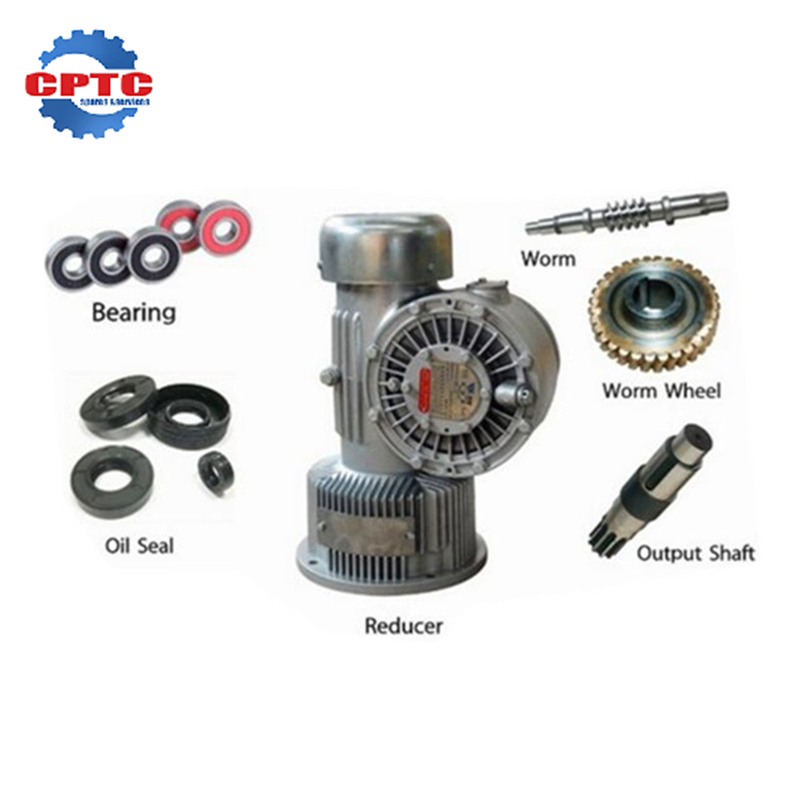
Hoist Gearbox Key Components and Their Potential Vulnerabilities
We have shown you a guide on the working process, selection, and maintenance tips of the hoist gearbox. To inspect a hoist gearbox properly, one should know its key parts and their potential weaknesses.
- Gear Teeth: These engaged components help in transmitting power inside the gearbox. Gear teeth over a period of time undergo wear, chipping, or pitting due to overloading, misalignment, or insufficient lubrication. Visual inspection may indicate obvious damage, while listening for unusual noises such as grinding and squealing may be indicative of more subtle issues.
- Bearings: Bearings accept the rotating gears of the gearbox, reducing friction and ensuring smooth operation. The most common of these are ball bearings, roller bearings, and needle roller bearings. Signs of bearing wear include excessive vibration, noise, and temperature. Regular lubrication is necessary to prevent premature bearing failure.
- Seals: Seals are used to keep out contaminants like dirt, water, and debris from entering the gearbox and to keep lubricant in. Leaking or worn-out seals will lead to lubricant loss, friction buildup, and accelerated component wear. Inspect seals for cracks, tears, or hardening, indicating a failed seal.
- Lubrication System: Proper lubrication is critical to the operation and life of a hoist gearbox. Lubricant shields the surface, reduces friction, and dissipates heat. These are signs of lubrication issues: excessive heat, unusual noise, and metal shavings in the lubricant. Routine oil analysis will be able to identify issues before they occur.

The Inspection Process of Hoist Gearbox
There may be many causes of gearbox gear failure, and we have to check and repair the gears carefully in order to achieve this. If there is a gearbox gear failure, you should first figure out the precise cause and take proper measures thereafter. In this way, we can enhance the routine working of the gear and extend the service life of the gearbox. The below will present some frequent causes of failure of the reducer gear in construction hoist:
A thorough inspection of a hoist gearbox entails a blend of visual, auditory, and instrumental methods.
Visual Inspection
The first thing to do when assessing the state of a gearbox is to conduct a thorough visual inspection. Look for signs of surface damage, such as cracks, dents, or corrosion on the casing. Check for lubricant leaks, which could be a sign of seal failure or inside damage. Check whether the gearbox is aligned with other equipment, since misalignment can lead to vibratory and excessive wear.
Listening Test
A seasoned inspector can often identify potential issues by listening to the operating gearbox. Unusual noises, such as grinding, squealing, or humming, can indicate worn gears, dented bearings, or other mechanical problems. Knowing the origin of the noise, the inspector can narrow down potential causes for the issue.
Overheat is usually a sign of underlying problems in a gearbox. With a non-contact infrared thermometer, the inspector can make measurements of the housing of the gearbox and its separate components, such as bearings and gears. An elevated temperature might indicate increased friction, improper lubrication, or misalignment.
Vibration Analysis
Vibration analysis is a highly useful diagnostic tool that can help identify mechanical problems prior to them becoming critical. By using a vibration meter, the inspector can measure the levels of vibration at various points on the gearbox. Excessive vibration could be a result of worn-out bearings, unbalanced rotors, or misalignment. By analyzing the vibration reading, the inspector can locate the cause of the problem and recommend the corrective actions required.

Common Gearbox Problems and Solution
Gear Tooth Wear
Gear tooth wear is a common issue that may lead to decreased efficiency, greater noise, and ultimately, failure of the gearbox. Overload, misalignment, inadequate lubrication, and fatigue of the material are common causes of gear tooth wear. The consequences of severe gear tooth wear are higher vibration, reduced load-carrying capacity, and possibly catastrophic failure. Repair options for gear tooth wear range from re-machining of the gears to complete replacement.
Bearing Failure
Bearing failure may be the result of a number of factors, including improper lubrication, contamination, misalignment, and overloading. Symptoms of bearing failure are vibration, noise, and temperature. At times, the bearing seizes, causing damage to the shaft and other components. Replacement of the failed bearing is usually the only solution.
Seal Leakage
Seal leakage can also lead to loss of lubrication, friction, and wear of internal components. Additionally, dirt can find its way into the gearbox, causing corrosion and further damage. Reasons causing seal leakage include age, temperature, mechanical failure, or improper installation. The repair methods include replacing the broken seal or the seal groove repair.
Lubrication Issues
Poor lubrication can develop increased friction, overheating, and equipment wear prematurely. However, excessive lubrication can lead to contamination and reduced efficiency. Proper care should be exercised in applying the correct lubricant type and amount and adhering to the manufacturing firm’s lubrication maintenance schedule. Regular oil analysis will help detect potential lubrication problems and act upon it accordingly.
Final Word
With the outlined in this article by CPTC, including visual inspections, listening tests, temperature checks, and vibration analysis, it is possible to maintain optimal gearbox performance and minimize downtime. Timely maintenance and proactive problem-solving are essential to prolong the life of your hoist gearbox and safeguard your operations.
Related Products
CCKB Construction Hoist Spare Parts
CCKB 3-phase switch
CCKB counter roller
Construction Hoist Gearbox and Parts
Trademark: CPTC, GJJ, PET, BAODA
Passenger…
Nord Motor & Nord Gearbox
Quality assurance
Rich products
CPTC supply
Construction Hoist Mast Section
Simple operation
Stable performance