Suspended platforms (also known as gondolas or temporary suspended access equipment) are essential tools in modern construction and building maintenance. From façade repairs to glass cleaning, they enable work at dangerous heights. But with great utility comes great risk.
Goal of this Guide:
Help you understand how suspended platforms work, what safety risks exist, and how to eliminate six major hazard sources using practical, inspection-ready solutions.
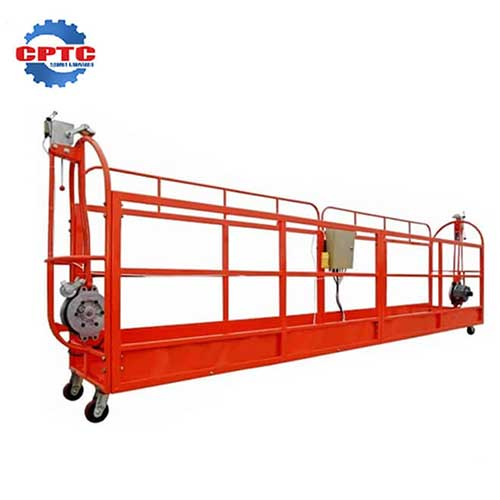

What is a Suspended Platform?
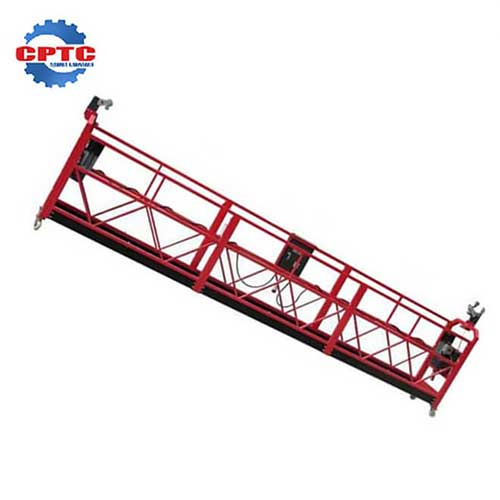
A suspended platform is a temporary aerial work structure, electrically powered, and suspended via steel wire ropes from a rooftop frame. It allows vertical movement for personnel during high-rise operations.
Key Structural Components
| Component | Function |
| Platform (Cradle) | Carries workers and tools; usually made of steel or aluminum |
| Suspension System | Includes rooftop supports, counterweights, and wire rope hangers |
| Hoists (Lifting Units) | Raise/lower the platform via gripping mechanism on ropes |
| Safety Devices | Prevent falls: includes locks, limit switches, anti-tilt systems |
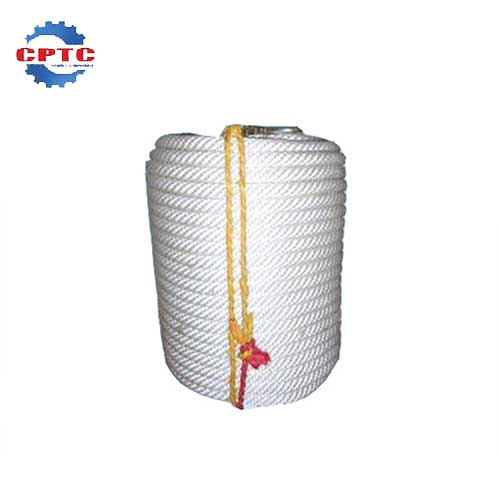
| Wire Ropes | Main and safety ropes made of high-tensile steel |
| Electrical Controls | Directs motion; emergency stop, directional controls, fault alarms |
6 Key Safety Production Hazards to Consider for Suspended Platforms

Structural Hazards: Platform Deformation or Rust
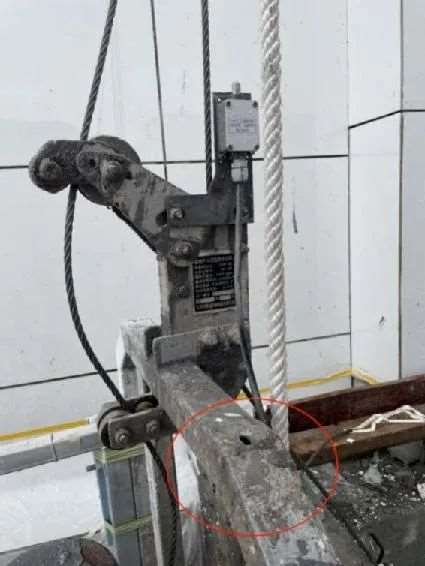
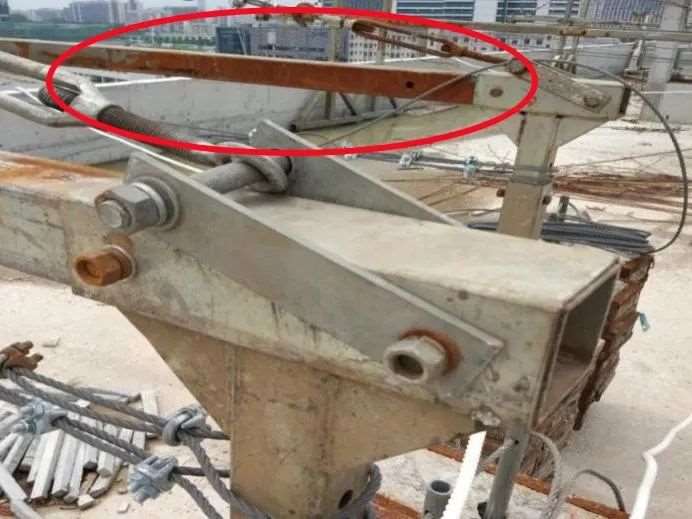


- Cause: Long-term exposure, overloading, or poor handling
- Risk: Structural collapse
- Tip: Inspect for cracks, weld failure, and joint looseness daily.
| Risk Factor | Symptoms | Action |
| Deformation | Bending, cracks | Replace affected parts immediately |
| Corrosion | Rust, pitting | Apply anti-corrosion treatment or replace |
Suspension System Hazards: Unstable or Incomplete Roof Supports
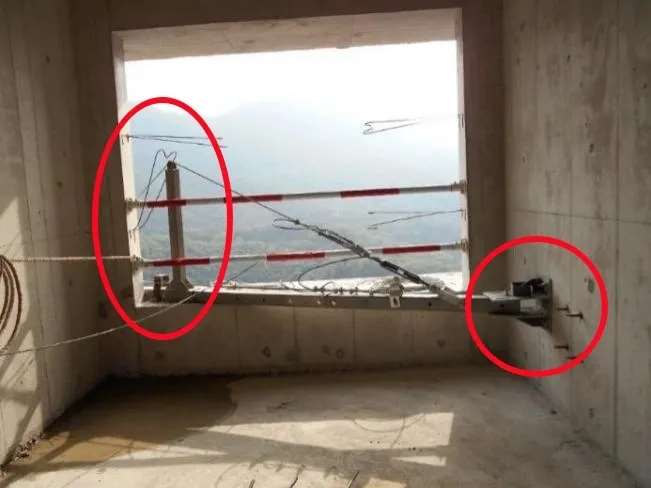

- Cause: Missing support frames, poor installation angle
- Risk: Tilting or detachment from the roof
- Tip: Measure vertical angle with a spirit level; check ballast match.
| Error Type | Solution |
| Missing front support | Install all manufacturer-specified parts |
| Wrong angle setup | Verify the correct ballast with a scale |
| Insufficient counterweight | Verify correct ballast with a scale |
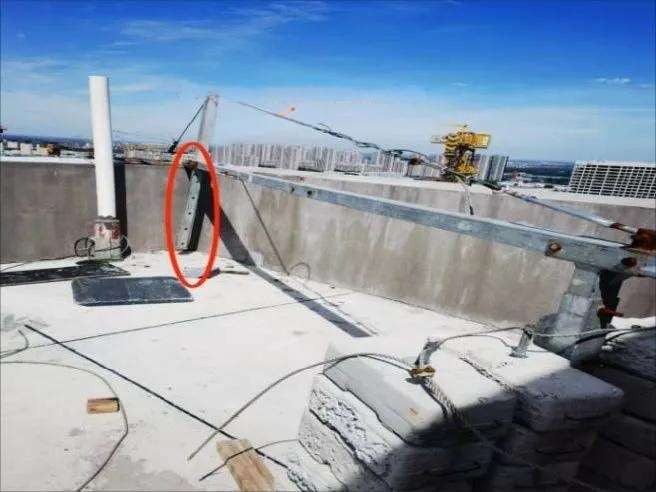
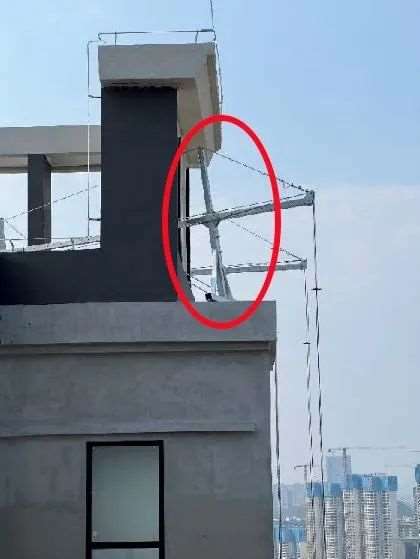
Guardrail & Fall Protection Hazards: Lack of Perimeter Safety Barriers
- Cause: Guardrails removed or never installed
- Risk: Falls from height or dropped tools
- Tip: Confirm guardrails are >1m high and withstand the required load force.
Fix
- Install guardrails, toe boards, and netting
- Use personal fall arrest systems (PFAS) with independent lifelines


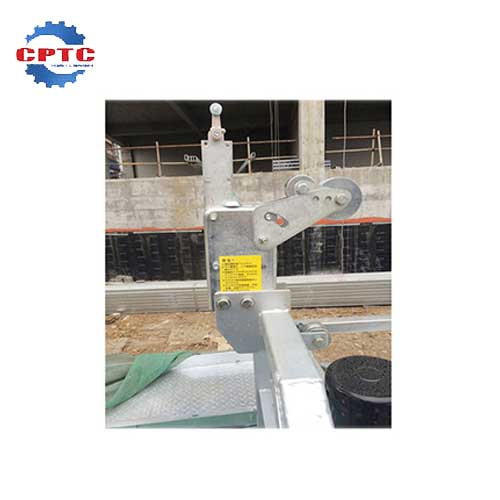
Safety Device Failures: Safety Lock or Limit Switch Malfunctions
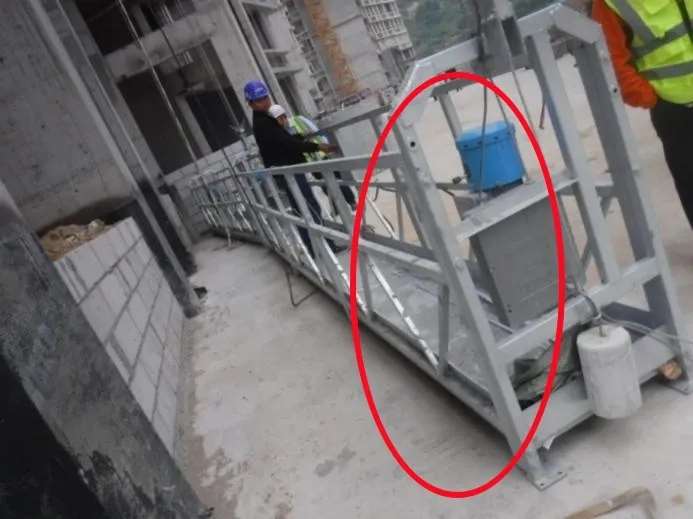

| Device | Fault | Consequence | Fix |
| Safety Lock | Doesn’t engage | Free fall risk | Test lock with slack rope simulation |
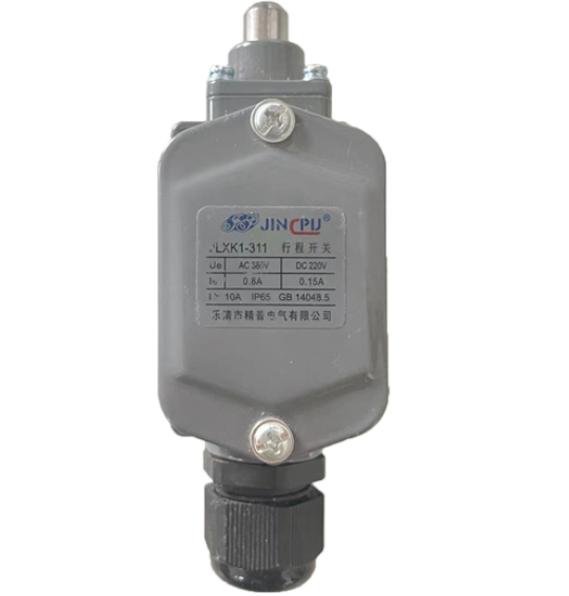
| Limit Switch | Doesn’t trigger | Overrun & collision risk | Manually test upper/lower limits |
Tip: Simulate faults during inspection to confirm real-world performance.
Hoisting System Hazards: Rope Misalignment or Hoist Failure
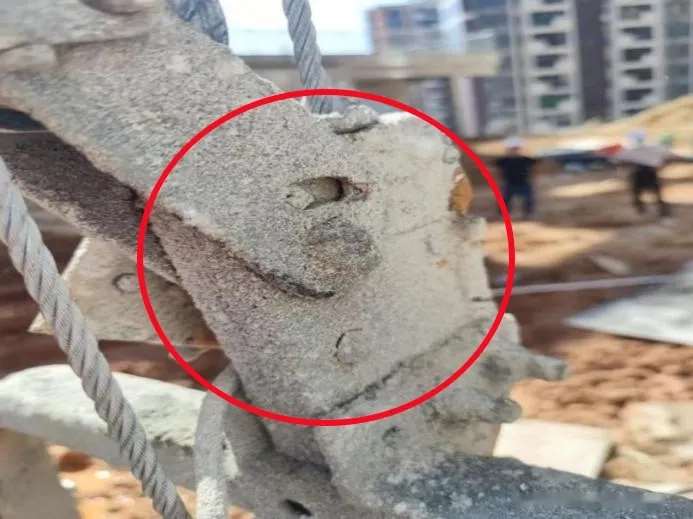
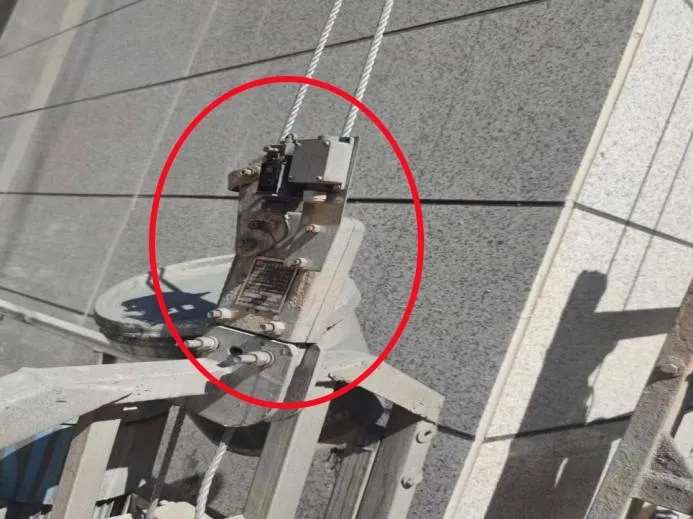
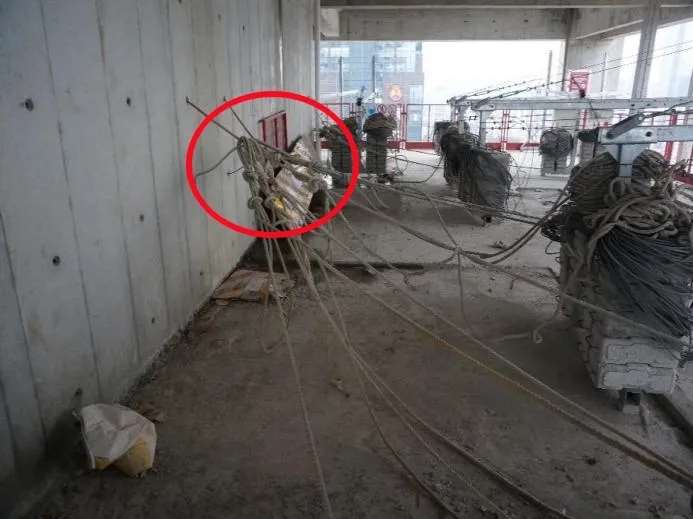



- Cause: Worn wire ropes, poor threading, loose hoist connections
- Risk: Jerky movement or total drop
- Tip: Verify that wire ropes spool evenly and hoist tension remains stable.
Fix:
- Realign the rope into the hoist groove
- Replace kinked or rusty ropes
- Tighten hoist bolts and check locking pins
Electrical System Hazards: Control or Grounding Failures
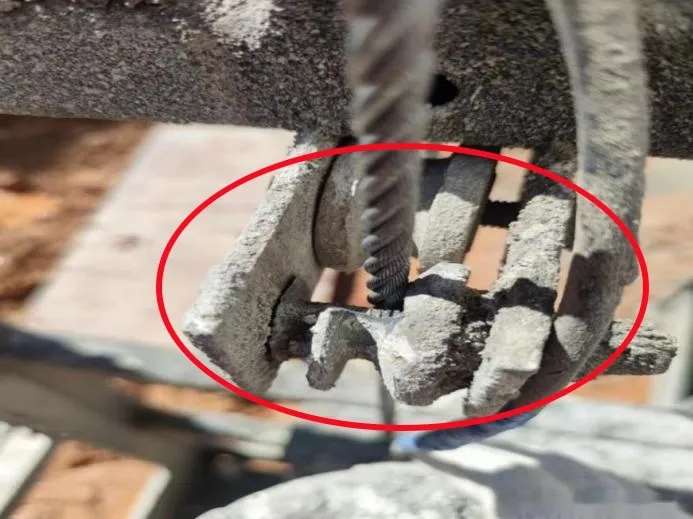
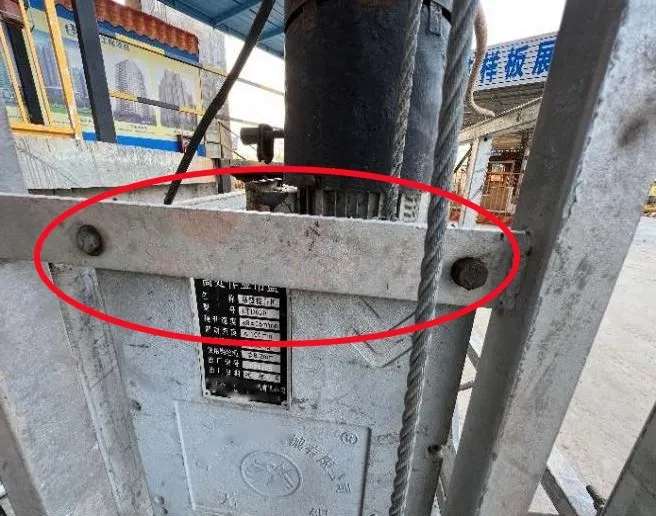


| Fault Type | Risk | Recommended Action |
| Exposed wiring | Electric shock | Re-insulate or replace damaged cables |
| Faulty controls | Unintended movement | Replace damaged switches or relays |
| Missing grounding | Severe injury risk | Ensure RCDs and grounding continuity tests pass |
Tip: Perform electrical insulation resistance test monthly.
Electrical System Hazards: Control or Grounding Failures
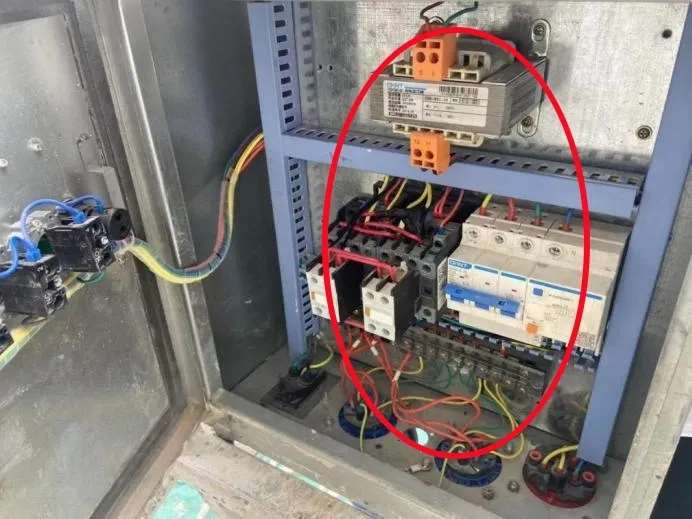
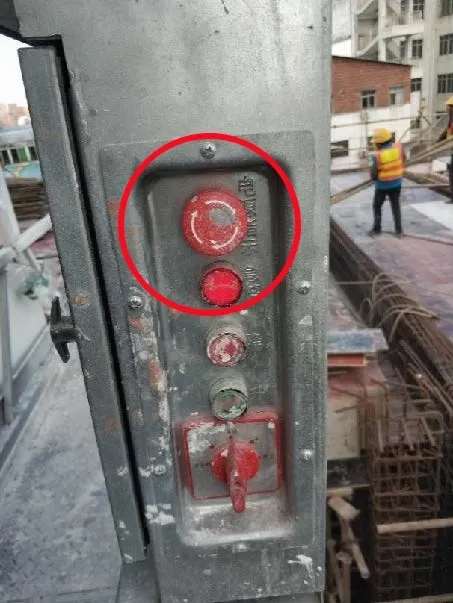


| Fault Type | Risk | Recommended Action |
| Exposed wiring | Electric shock | Re-insulate or replace damaged cables |
| Faulty controls | Unintended movement | Replace damaged switches or relays |
| Missing grounding | Severe injury risk | Ensure RCDs and grounding continuity tests pass |
Tip: Perform electrical insulation resistance test monthly.
Conclusion
Working on suspended platforms requires more than just skill—it demands discipline in safety and inspection. Every overlooked defect can lead to a fatal incident. By systematically identifying and solving hazards across all six categories, you protect not only your workforce but also your project timelines and compliance status.
Related Products
ZLP Series Suspended Platform
Simple and quick installation
Multiple security measures
Stable and…
Suspended Platform Safety Lock
Easy to Operate and Use
Made…
Limit Switch
Compact and Lightweight
Easy Installation
Safety Rope
Lightweight and Portable
Durable and Long-lasting